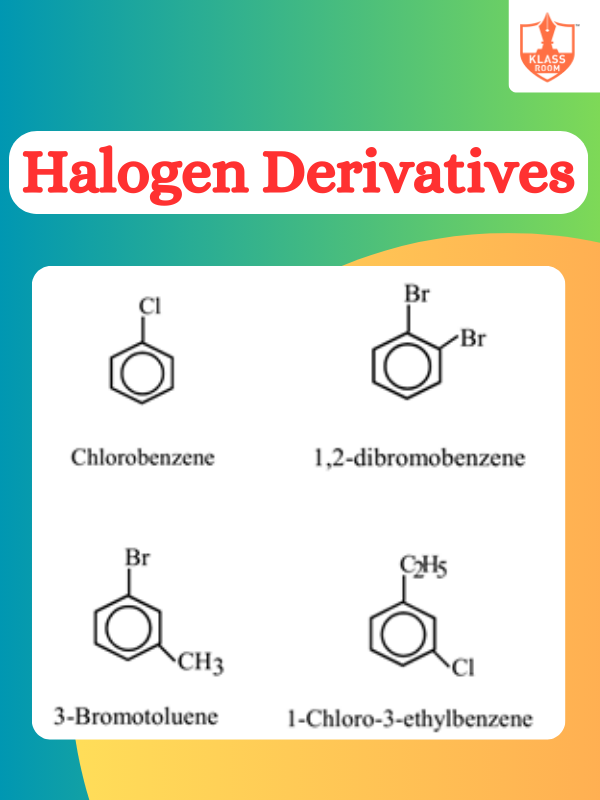
Contents

Gravitation
Description: Gravitation describes the force attracting objects with mass towards each other in the universe.

Description: Gravitation describes the force attracting objects with mass towards each other in the universe.




Board: CBSE
Stream: Science
Standard: XII
Course: Physics
Know More


Board: State Board
Stream: Science
Standard: XII
Course: Physics
Know More
Board: State Board
Stream: Science
Standard: XII
Course: Physics
Know More