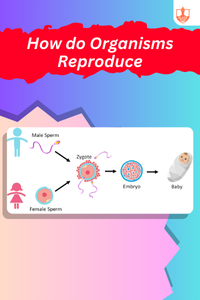
Related Courses

Introduction to Biotechnology
Board: State Board
Stream: Science
Standard: IX
Course: Science
Know More

Life Processes in Living Organisms
Board: State Board
Stream: Science
Standard: IX
Course: Science
Know More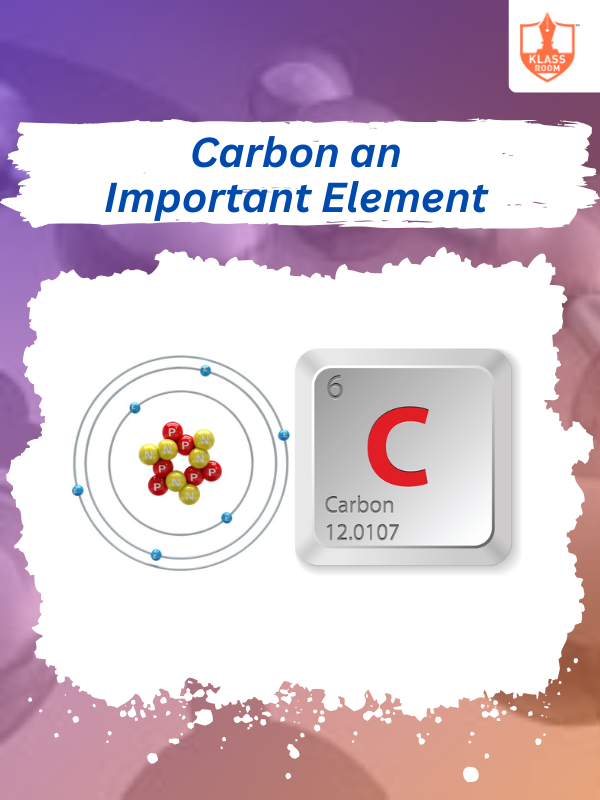
Carbon an Important Element
Board: State Board
Stream: Science
Standard: IX
Course: Science
Know More