Contents

Communication - Focus & Attention
Description: Listening for Understanding, Focus, and Attention are key for effective communication, helping to overcome barriers like distractions, misunderstandings, and lack of engagement, fostering clarity.

Communication - Case Study
Description: A case study involves detailed analysis of a specific instance, prompting questions to explore underlying issues, solutions, and outcomes.
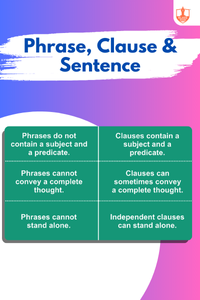
Sentence Types and Direct-Indirect, Active-Passive Speech : Phrase, Clause & Sentence
Description: A phrase is a group of words without a subject-verb pair, a clause includes a subject and verb, and a sentence is a complete thought.
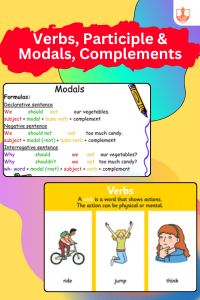
Sentence Types and Direct-Indirect, Active-Passive Speech - Verbs, Participle & Modals, Complements
Description: Verbs indicate actions or states. Participles are verb forms used as adjectives. Modals express abilities or possibilities. Complements complete the meaning of a predicate.

Sentence Types and Direct-Indirect, Active-Passive Speech : Subject-Verb Agreement
Description: Complements complete predicates. Sentences are classified by structure as simple, compound, complex, or compound-complex. Subject-verb agreement ensures subjects and verbs match in number.

Sentence Types and Direct-Indirect, Active-Passive Speech - Practice Exercise & Tenses
Description: Practice exercises in tenses improve understanding and correct usage of past, present, and future forms.

Sentence Types and Direct-Indirect, Active-Passive Speech - Active Passive Voice & Direct & Indirect Speech
Description: Active voice highlights the subject's action. Passive voice shifts focus to the object. Direct and indirect speech convey spoken words.
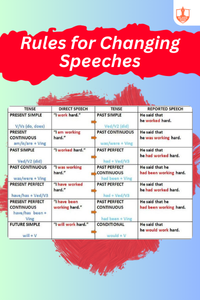
Sentence Types and Direct-Indirect, Active-Passive Speech - Rules for Changing Speeches
Description: To change direct to indirect speech, adjust pronouns, verb tense, and expressions of nearness to distance. Exclamatory sentences convert to statements or expressions with exclaimed or said.
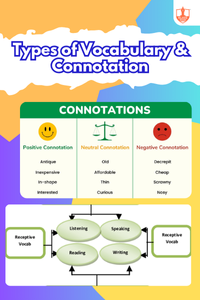
Vocabulary - Types of Vocabulary & Connotation
Description: Types of vocabulary: active (used regularly), passive (understood but not used), and academic (specialized knowledge). Connotation adds emotional nuance.

Vocabulary - Jargon & Synonyms & Antonyms
Description: Jargon: specialized terminology within a field. Business jargon includes terms like synergy or leverage. Synonyms are words with similar meanings; antonyms have opposite meanings.

Vocabulary - Collocations & Idioms
Description: Roots of words form their core meanings. Loanwords are borrowed from other languages. Prefixes and suffixes modify roots. Phrasal verbs, collocations, and idioms enrich language usage.


.png)



.png)
.png)
_(1).png)


.png)
