Contents

Tissues
Description: Tissue consists of cells with similar functions; meristematic tissue is responsible for plant growth, containing undifferentiated cells capable of division.
Permanent Tissue
Description: Permanent tissue consists of cells in plants that have ceased dividing, providing support, protection, and carrying out specialized functions indefinitely.
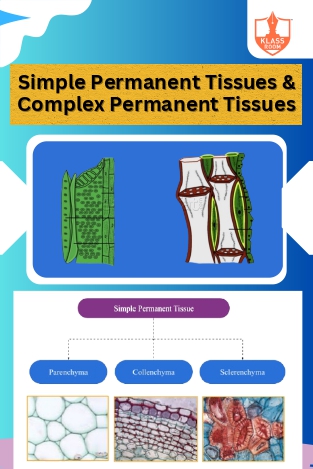
Simple & Complex
Description: Simple permanent tissues include parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma, while complex permanent tissues are xylem and phloem, conducting water and nutrients.
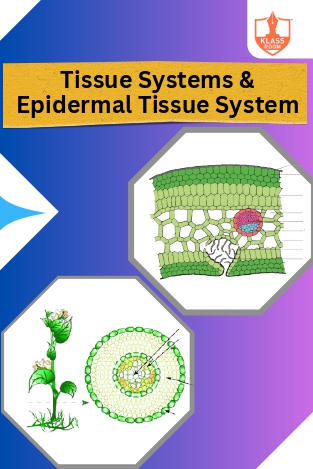
Tissue System
Description: Tissue systems are groups of tissues with similar functions. The epidermal tissue system is the outermost protective layer in plants.
.jpg)
Anatomy
Description: Dicot roots have a central vascular cylinder, while stems exhibit vascular bundles arranged in a ring. Monocots lack secondary growth.

Leaves
Description: Dicot leaves have branching veins, a palisade and spongy mesophyll. Monocots have parallel veins, and vascular bundles are scattered.

Wood & Cork
Description: Wood is secondary xylem, providing structural support in trees. Cork cambium produces cork cells, forming the protective outer bark.

Growth
Description: Secondary growth in roots involves the formation of secondary xylem and phloem, increasing girth and supporting long-term growth.